Solid or liquid complexes and chelates?
Why liquid chelates are better than spray-dried granulates in many applications.
The intention of this article is to highlight the structural, process and agronomic advantages in the use of aqueous concentrates. If this finds your interest, here is our complete programme of liquid EDTA-/DTPA-/ EDDHSA-/HEDTA-/HGA-micronutrient chelate and complex compounds linked to it: plant-nutrients.
Solid chelates,e.g. EDTA-FeNa (CAS 15708-41-5) or EDTA-ZnNa2 (CAS 73513-47-0), are formulated as Sodium salts. As such, they have the advantage of being based on relatively cheap raw materials. But on the other hand, they have limited solubility.
- A useful example to demonstrate is the solid type of EDTA-FeNa, 13 % Fe, which shows a pH value in water of approximately 5 and a solubility of just 90 g/L, i.e. less than 1.5 % Fe w/w.
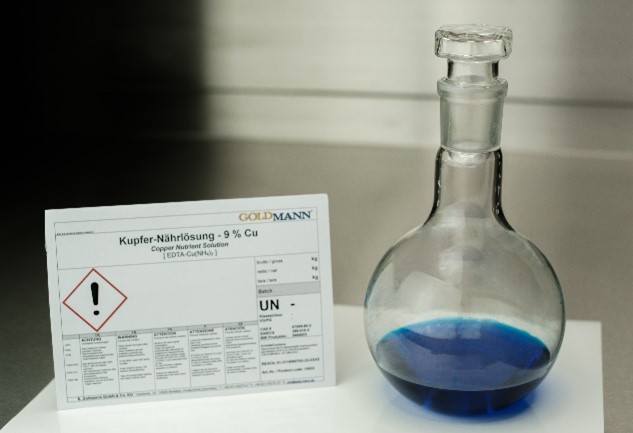
- Our EDTA-Iron-Nutrient-Solution (EDTA-FeNH4 x NH4OH, CAS 68413-60-5), on the other hand, is almost pH neutral, offers stably 7.5 % Fe in aqueous solution and provides a small bio-available nutrient share of nitrogen.
The solid Na-containing EDTA chelates are therefore preferably used as nutrient salt additives and this way dedicated for trace element supplements added into soluble NPKs.
Our EDTA-based nutrient solutions and trace element mixes thereof are formulated either as Potassium or Ammonium salts and are thus highly concentrated.
They are water-miscible in any form and withstand the presence of phosphate and carbonate up to the alkaline range. In addition, they can be mixed with each other in any ratio and thus allow the almost unlimited formulation of liquid trace element mixtures or liquid complete fertilizers. It is no surprise they are widely used in high-value crop cultivation and seed drenching.
Due to the scarcity and rising cost of fossil fuels, the energy-intensive drying of water-soluble products will tend to decline, provided that the transport distances of the concentrated aqueous solutions are sufficiently short.
In the current market situation, the imported solid chelates appear cheaper in terms of trace element content. In the medium term, however, the domestic production, versatility (ready-to-use) and better bioavailability will prove advantageous.
Have we aroused your interest? Then please do not hesitate to contact us. Gladly by phone or email.